

Lesson Objective: All of the substances on Earth are composed of unique combinations of atoms. Tap water, even bottled water, is a mixture of elements, compounds, and H2O molecules. To make clean water, we use filtration and other separation techniques.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make broader connections:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
We can use the water filtration system that is used for camping trips. The water from the beach will go into the filter and it will make the water clean.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Human activities have devastated much of the hydrosphere and, in turn, the biosphere. With much of Earth’s accessible freshwater devastated by human activity, water pollution is responsible for millions of deaths annually.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Research
Discourse Debrief activity:
[Tip: Consider completing a KWL chart (from Peartreeedu, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons) with your class so scholars can reflect on their prior knowledge and become invested in new questions to be answered throughout the unit.]
Introduce the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
I think that the cleanup of polluted water should be a priority for scientists. I think this because I know that water pollution has negative effects on the environment and many living things, including humans. For example, people need clean water to drink and bathe in, and without access to clean water, many people die each year.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties that can be used for their identification. Filtration is an effective method for separating solids from liquids. Strainers and filter paper separate mixtures based on their particle size. Understanding the properties of the materials in a mixture allows scientists to develop effective procedures for separating them.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
[Materials Management Tip: Leave extra time for scholars to clean up at the end of this investigation.]
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Sahara has a mixture of 1,000 large and small paper clips. She has these following items in her kitchen:
1.Sahara decided to use a funnel to separate the large paper clips from the small paper clips. Explain why a funnel is not the best tool for separating the paper clip sizes. [1]
I think the funnel will not be the best tool for separating the paper clip sizes because the hole in the funnel is too big. The funnel will allow any size paper clip to go through the hole, so it will not separate the bigger ones from the smaller.
2.Circle the tool above that best separates the paper clips by size. [1]
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Despite its apparent disappearance, a substance dissolved in a mixture often retains its chemical properties. Distillation can separate a dissolved solid from water.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Make broader connections:
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Directions: The picture shows an experimental setup to separate a salt, sand, and water mixture by filtration.
1.Salt and sand are approximately the same size. Will the experimental setup shown above separate the solutes (sand and salt) from the solvent (water)? Put an X on the statement you agree with most. [1]
Filtration will separate both salt and sand from the water. |
|
Filtration is not enough to separate both sand and salt from the water. |
2.Why or why not? Explain your choice. In your explanation, address both the sand and the salt. [2]
Filtration will be able to separate sand from the salt and water because the sand is too big to pass through the filter. The sand does not dissolve in water, but salt does. The water carries the dissolved salt through the filter; therefore, filtration is not able to separate both salt and sand from the water.
3.Identify the components in the filtrate that would be present after pouring the mixture through the filter. [1]
Salt dissolved in water.
Salt and water.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Some liquids can be separated through the process of decantation because of their different densities. Oil and water are immiscible and instead form layers. Once immiscible liquids settle in a separatory funnel, liquids layer from least dense (top) to most dense (bottom).
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Make broader connections:
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Directions: The cup pictured below contains a mixture of the following three immiscible liquids: honey, dyed green water, and blue dish soap. Table 1 lists the physical properties of those substances.
1.Which layer would you expect to find each substance in the cup? [1]
2.If the liquids were not immiscible, could you use decantation to separate this mixture? Circle the most correct explanation. [2]
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Multiple techniques must be used to separate more complex mixtures. To separate a mixture efficiently, you must understand the physical properties of its ingredients. Filtration and decantation rely on differences in physical properties. Filtering uses particle size to separate materials, while decanting relies on differences in densities.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
1.José has a mixture of marshmallows, sugar, and water. The sugar has dissolved into the water. List two materials José would need to separate his mixture. [2]
Sieve for filtration
Pot for distillation
2. Explain why he would need both of these materials. [2]
The solid marshmallows can be easily removed using filtration, but the dissolved sugar will need to be removed through distillation. Using these materials will ensure that Jose is able to separate all three ingredients from the mixture.
3.Identify two substances that you think could be separated using decantation. Explain your reasoning. [2]
I think oil and vinegar could be separated using decantation. If left to sit out, the oil would settle on the top, leaving the vinegar on the bottom. Then, the oil could be poured off. I chose these two liquids because I believe they have different densities.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: You cannot just combine any two materials to create a solution. Only certain materials are able to dissolve in others because of their polarity. Polarity affects attraction between molecules, which affects solubility. In most cases, like dissolves like: polar dissolves polar, and nonpolar dissolves nonpolar. An example of an excellent polar solvent is water. When an object dissolves, the molecules are still there but are dispersed within the solvent, making them impossible to see.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Ask: How could this knowledge help scientists clean poisoned water?
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Directions: The following table lists the physical properties of the following substances. Use the following information, Table 1, and your knowledge of science to answer the question below.
Table 1: Physical Properties of Substances in Water
1.Which compounds are polar, nonpolar, and soluble/not soluble in water? Fill in the blanks in Table 1. [3]
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: It is possible to change the speed at which a solute dissolves. Increasing temperature and agitation both increase the rate of solubility.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
•Follow the Do Now plan.
Launch
•Ask: When an oil spill or other source of pollution is identified in a body of water, why do you think scientists want to clean it up as fast as possible?
•Show pictures of the negative results of water pollution on the biosphere, such as these:
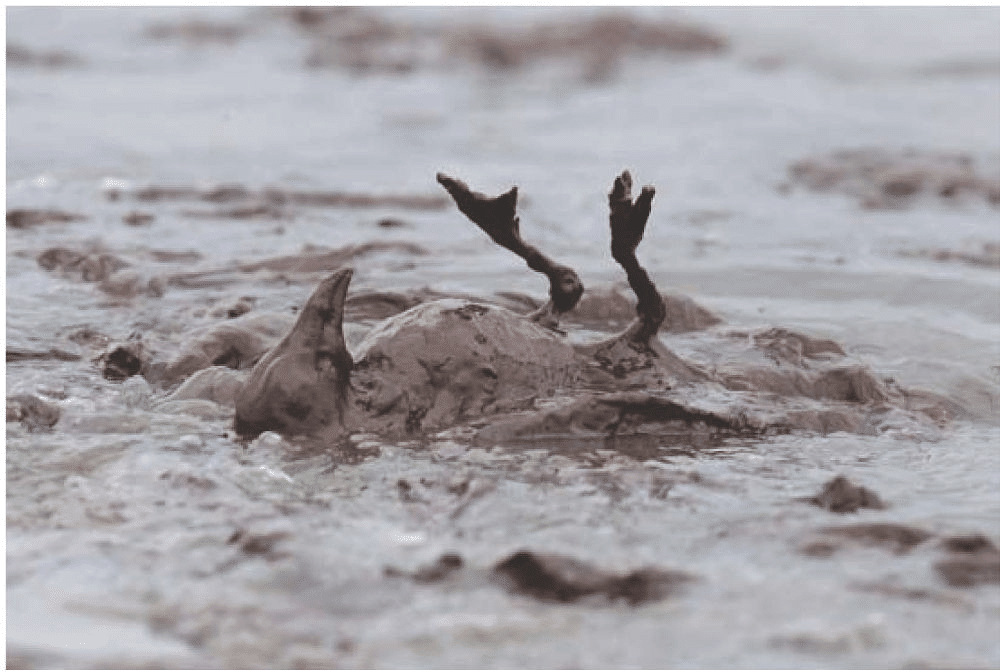

Image Credit: “A dead bird covered in oil from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, East Grand Terre Island, Louisiana, June 2010,” Charlie Riedel AP/Shutterstock.com via Encyclopedia Britannica
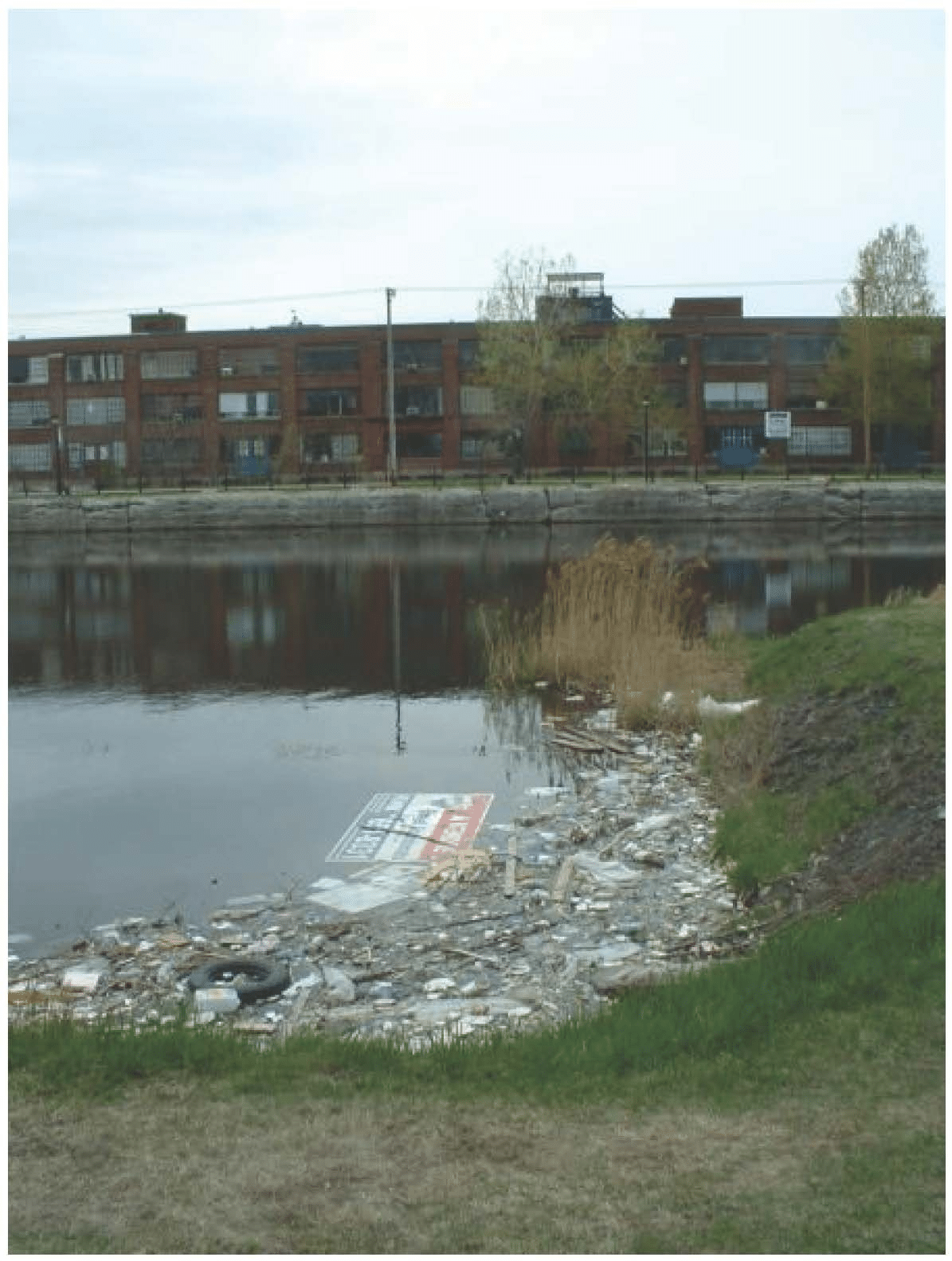

Image Credit: “Pollution in the Lachine Canal, in Montreal,” Aarchiba, public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
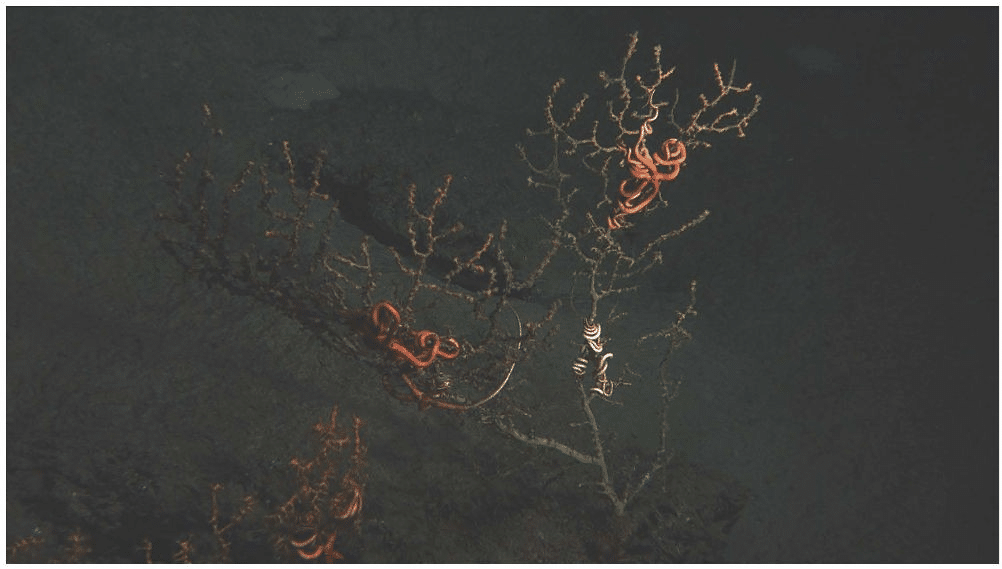
Image Credit: “Coral colony in the Gulf of Mexico affected by the 2010 oil spill,” Lophelia II 2010 Expedition, NOAA-OER/BOEMRE), public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Kyra is experimenting with hot chocolate mix at home. She places the mix into a cup of water.
Krya could stir the mix or place the mixture of hot chocolate mix and water in the microwave. Heating and agitation both increase the rate of solubility.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: The changes in solubility that occur with variations in temperature or pressure can be described and predicted. Temperature can have modest or drastic impacts on solubility depending on the substance. Solubility curves tell us how temperature affects solubility, how much solute we would expect to be dissolved or not dissolved, and the relative polarity of molecules.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Activity
Discourse Debrief activity:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Scholars were studying the solubility of four substances using the graph shown. Use the image below to answer questions one through three.
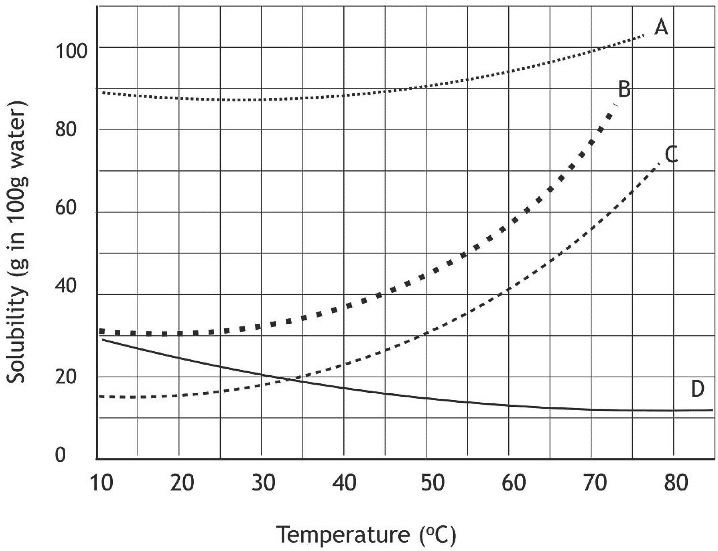
Image Credit: Brightyellowjeans, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
1.At which temperature was approximately 20 g of Substance C and Substance D dissolved? [1]
1.10℃
2.27℃
3.33℃
4.42℃
Rafael is trying to dissolve 100 g of Substance A in Beaker 1 and 100 g of Substance B in Beaker 2 at room temperature (23℃) but only some of each compound dissolves.
2.Which compound would benefit the most with an increase in temperature? [1]
Substance A |
|
Substance B |
3.How do you know? Explain why. [1]
Possible Exemplars:
Substance B has the steepest curve on the graph, which indicates temperature affects Substance B solubility greatly.
Substance B is most affected by a change in temperature. This dramatic change was represented by the steepest curve on the graph.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: When confronted with an unfamiliar mixture, scholars should study the physical properties of the ingredients to help determine the best method of separating them.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
[Behavior Management Tip: Set clear behavioral expectations for this investigation.]
Experiment
Discourse Debrief experiment:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Make broader connections:
Accountability (Lab Notebook)
Density allowed us to separate the gold. Gold is denser than the dirt, sand, and rocks with which it is mixed. It sinks to the bottom because it is denser, so we can decant the other materials.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Gases, like solids, can also be dissolved in liquids. Gases can be separated via changes in temperature, the solubility of gases decrease as temperature increases. The changes of state that occur with variations in temperature or pressure can be modeled and predicted.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Activity
Discourse Debrief activity:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
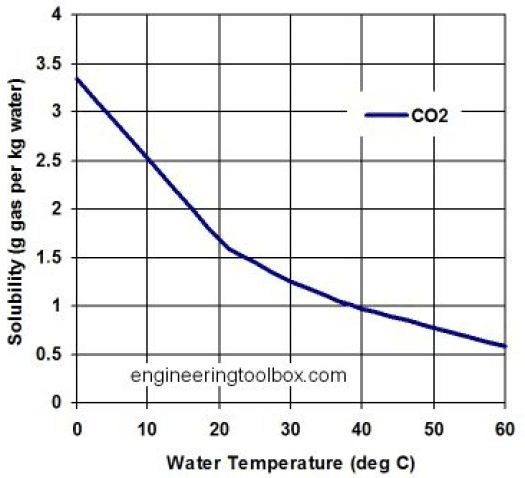
Image Credit: “Solubility of CO2 in water” from The Engineering Toolbox (multiple authors), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Accountability (Exit Ticket) Directions: Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
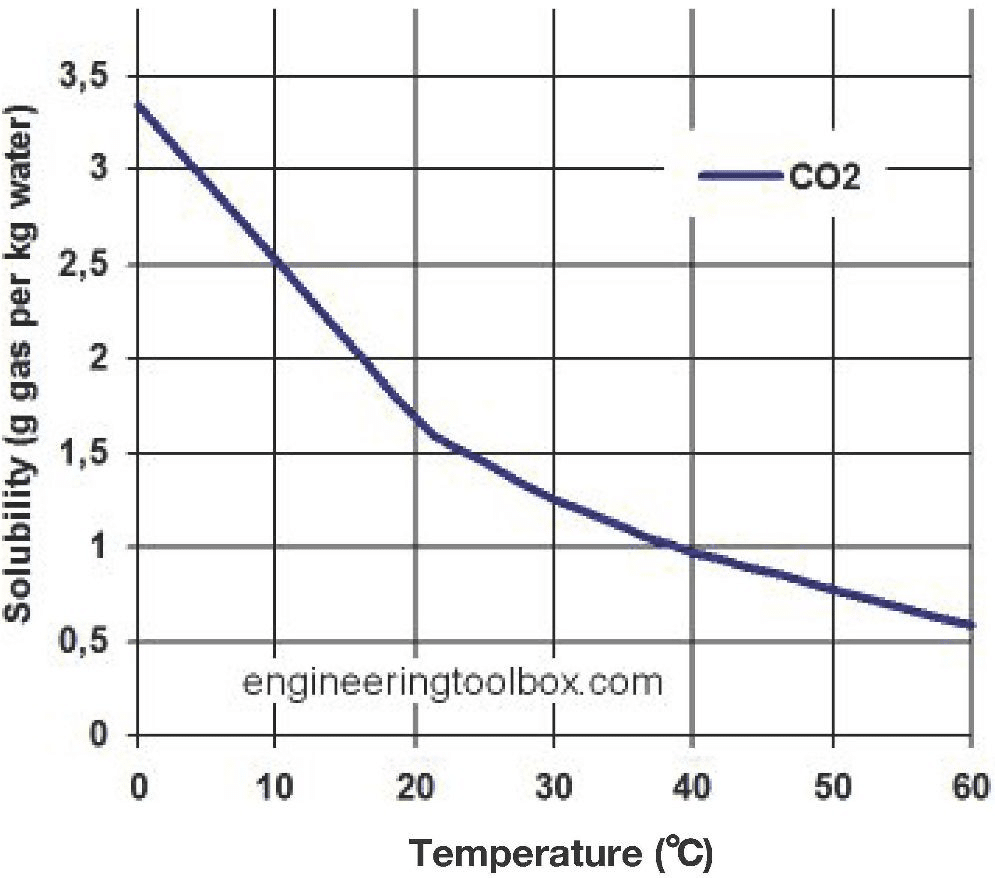
Image Credit: “Solubility of CO2 in water,” The Engineering Toolbox (multiple authors), public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Researching the properties of materials provides scientists with more information to plan a multistep solution to a complex problem. Engineered designs should be justifiable using science.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Activity
Discourse Debrief activity:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
Our group plans to remove the peppercorns by using a filter. Because the peppercorns are solid and did not dissolve in the water, we think we can remove those with a strainer. Additionally, our group plans to use a separatory funnel to remove the oil from the water. Because they have different densities and are layered, we think we can separate the oil to remove it. We are confident in these methods because of our understanding of physical properties.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Do Now
Launch
Activity
Discourse Debrief activity:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Lab Notebook)
Scoring Award points as follows:
Lesson Objective: Performance of a design can be optimized by prioritizing criteria, making tradeoffs, testing, revising, and retesting. By studying the physical properties of a substance, scientists can choose a successful method for isolation.
Materials Needed
Prep
What are scholars doing in this lesson?
Do Now
Launch
Activity
[Materials Management Tip: Leave ample time for cleanup, as scholars will need extra time to ensure their tables are clean and wiped down after this investigation.]
Discourse Debrief activity:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
Tomorrow, we want to use tulle to filter the mixture. Today, we only used a strainer, which has larger holes; it was not able to effectively remove all the smallest particles. Swapping the strainer for the tulle allows us to further isolate the solid particles from the water.
Scoring Award points as follows:
Do Now
Launch
Activity
Discourse Debrief activity:
Make connections to the Essential Question:
Accountability (Exit Ticket)
| Oil and Water Mixture | Salted Water |
|---|---|
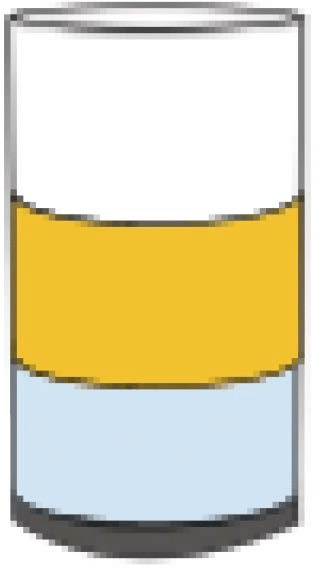 Separation Technique: Decantation |
 Separation Technique: Distillation |
| Lemonade Powder Drink | Coffee Grounds and Coffee |
|---|---|
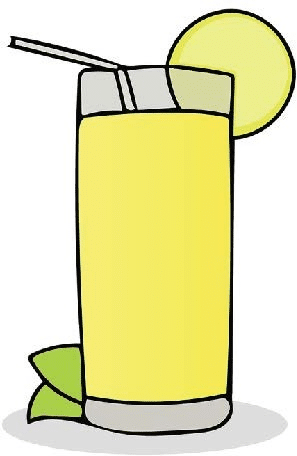 Separation Technique: Distillation |
 Separation Technique: Filtration |
Scoring Award points as follows:
Vocabulary List
resources
Access a wide array of articles, webinars, and more, designed to help you help children reach their potential.

The K-1 Counting Jar Toolkit
Educator
Curriculum
Elementary School
1st
K
Math
Curated Middle School Novel List (Grades 5-8)
Educator
Parent
Book lists
Book Lists
Middle School
5th
6th
7th
8th
Literacy

ES PBL Grade 2: Brooklyn Bridge
Educator
Curriculum
Elementary School
2nd
PBL

ES PBL Grade 3: Iroquois and Lenape
Educator
Curriculum
Elementary School
3rd
PBL
NEWSLETTER
"*" indicates required fields
